
Feb 24, 2026
- Products & Solutions
- Press Releases
Nov 14, 2019
Products & Solutions / Press Releases
This technology contributes to the realization of a sustainable society by helping facilitate reuse and recycling of lithium-ion batteries.
Osaka, Japan – Panasonic Corporation (Panasonic) announced today that it has developed a new battery management technology that measures a battery's electrochemical impedance[1], which is an effective method of evaluating the residual value of lithium-ion batteries in devices.
This technology is expected to be applied to various devices that use lithium-ion battery modules with many battery cells stacked in series and to future vehicles. Panasonic has developed this technology in collaboration with Professor Masahiro Fukui of Ritsumeikan University. Panasonic developed a new battery monitoring IC (BMIC) test chip, measurement algorithm, and software, while Ritsumeikan University evaluated the performance using actual batteries.
Current applications of lithium-ion batteries are expanding to the field of industrial devices and mobility, and the importance of reuse and recycling is also increasing. The newly developed battery management technology makes it possible to measure electrochemical impedance using the AC current excitation method[2] for lithium-ion stacked battery modules that are installed in operating devices. Furthermore, this technology aims to enable the evaluation of residual value by way of a deterioration diagnosis and failure estimation based on an analysis of acquired measurement data. This will contribute to the realization of a sustainable society where future lithium-ion batteries can be reused and recycled.
Conventional electrochemical impedance spectroscopy is widely used as a non-destructive method for evaluating lithium-ion batteries. This measurement method requires an application specific measuring instrument and a large thermostatic chamber that keeps the temperature of the battery constant, and it was necessary to measure each cell in the laboratory.
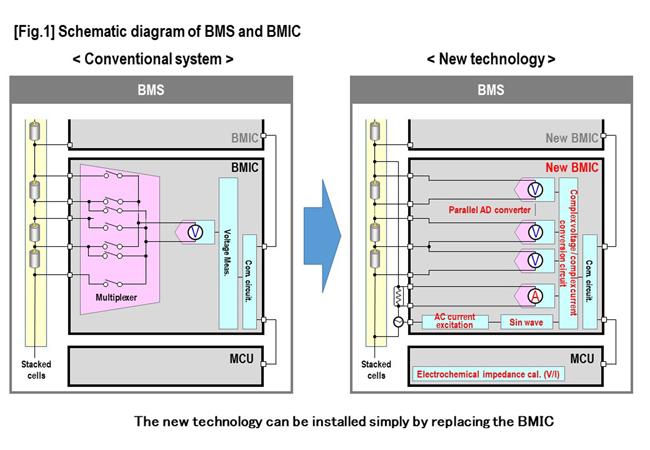
Conventional BMIC measures the individual battery voltage of 6 to 14 lithium-ion battery cells stacked in series. By using multiple BMICs, BMS acquires battery cell voltage data from several up to 200 cells connected in series, monitors the battery, and ensures its safe use. In addition, BMS calculates the remaining driving range and usable time by estimating the state of charge (SOC[3]) and the state of health (SOH[4]).
The newly developed BMIC test chip has a built-in electrochemical impedance measurement function using the AC current excitation method in addition to these conventional functions. The electrochemical impedance measurement is achieved by 15 fully parallel analog / digital converters and an AC current excitation circuit with pulse modulation from 0.1 Hz to 5 KHz and a complex voltage / complex current conversion circuit built in the BMIC. Therefore, the BMIC chip can measure the electrochemical impedance of a battery in operation without significantly changing the configuration of the current BMS installed in the battery.
State estimation by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy is performed by measuring the Cole-Cole diagram[5] drawn with complex impedance. Ritsumeikan University measured cylindrical lithium-ion battery cells using BMIC and measurement software developed by Panasonic. As a result, it was confirmed that the Cole-Cole diagram can be measured in the frequency range from 1 Hz to 5 KHz with the same accuracy as the standard measuring instrument used in the industry.
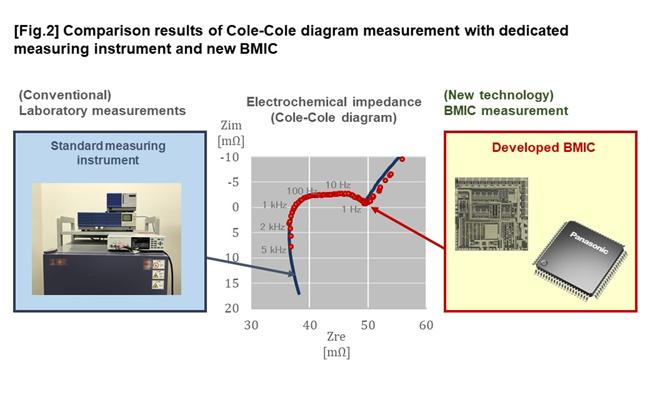
The electrochemical impedance of lithium-ion batteries is very sensitive to temperature changes. For this reason, measurements using dedicated measuring instruments in the laboratory are performed by placing the battery in a thermostatic chamber that maintains a constant temperature. The battery module in operation could not achieve a stable measurement of electrochemical impedance because the environmental temperature changed. Therefore, Ritsumeikan University and Panasonic developed a temperature correction technology that measures the temperature of the lithium-ion battery during the electrochemical impedance measurement, corrects the temperature change of the impedance to the standard temperature, and draws it on the Cole-Cole diagram.
This makes it possible to accumulate Cole-Cole diagrams normalized to the standard temperature in the database even when the environmental temperature varies depending on the season and time.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy is widely used as a non-destructive method of evaluating lithium-ion batteries. This measurement method requires an application specific measuring instrument and a large thermostatic chamber that keeps the temperature of the battery constant, and it was necessary to measure each cell in the laboratory.
Devices and vehicles that use multi-cell stacked lithium-ion batteries. Electric bikes, LSVs (Low-Speed Vehicles), construction and logistics machinery, etc. In the future, electric vehicles, large-capacity storage batteries.
Ritsumeikan University Fukui Laboratory, joint research partner, made two presentations at the 60th Battery Symposium. This symposium is being held from November 13 (Wed) to 15 (Fri), 2019 by the Committee of Battery Technology, the Electrochemical Society of Japan, at Kyoto International Conference Center (Takaragaike, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto City).
AC resistance obtained by dividing the AC voltage of the battery by the AC current. The unit is the same ohm used to express DC resistance. Expressed as a complex number by Laplace transform.
Also called AC superposition method. Similar to network analysis, a method of measuring the frequency characteristics of AC impedance by applying AC current while sweeping the frequency.
Battery charge rate. SOC is a percentage of the remaining capacity with respect to the full charge capacity.
Capacity maintenance rate. SOH is the ratio between the initial charge and the amount of charge that has deteriorated over time. The amount of charge is measured by the current integration method (Coulomb counting), etc. by BMS. The current SOH can be calculated by storing the charge amount at the start of use and comparing it with the current charge amount. However, SOH has no direct correlation with various lithium-ion battery deterioration phenomena such as electrode deterioration due to metal lithium deposition (dendrites) and electrolyte deterioration. Therefore, the SOH measurement is for obtaining the current charge amount, it cannot estimate the future SOH, and is different from the deterioration diagnosis.
Cole-Cole diagram is a complex representation of the AC impedance, and the frequency sweep trace is plotted on the complex plane. Also called Nyquist diagram. Often used in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to analyze changes in the internal AC impedance of battery cells. Named after the inventors KENNETH S. COLE and ROBERT H. COLE.
Panasonic Semiconductor Solutions Co., Ltd.
https://www.panasonic.com/jp/company/pscs/en/contact.html?ad=press20191114
Panasonic Corporation is a worldwide leader in the development of diverse electronics technologies and solutions for customers in the consumer electronics, housing, automotive, and B2B businesses. The company, which celebrated its 100th anniversary in 2018, has expanded globally and now operates 582 subsidiaries and 87 associated companies worldwide, recording consolidated net sales of 8.003 trillion yen for the year ended March 31, 2019. Committed to pursuing new value through innovation across divisional lines, the company uses its technologies to create a better life and a better world for its customers. To learn more about Panasonic, visit https://www.panasonic.com/global.
The content in this website is accurate at the time of publication but may be subject to change without notice.
Please note therefore that these documents may not always contain the most up-to-date information.
Please note that German, Spanish and Chinese versions are machine translations, so the quality and accuracy may vary.