Osaka, Japan - Panasonic Corporation today announced that it has developed a semiconductor white light source capable of outputting luminous flux in the 10,000-lumen[1] class. This newly developed technology will enable wider variation in design, a higher brightness and smaller form factor in applications in areas such as data projectors and vehicle headlights.
In this development, an increased light output was achieved due to the high-efficiency, low-loss design and modularization of the near-ultraviolet semiconductor laser used in the light source. A high luminous flux of white light was realized through the development of a phosphor material that is not subject to luminance saturation[2] even when irradiated with high-intensity laser light. The use of a laser with a smaller light-emitting area and superior light emission directionality to LEDs has made a compact optical configuration that boasts higher brightness and a smaller form factor possible. This technology opens the way to the greater use of semiconductor light sources in the projection/lighting market.
The developed technology has the following features:
- By increasing the output of the near-ultraviolet laser in the light source, to 10-times that of a conventional laser*1, the industry's highest*2 light output of 60 watts has been achieved. The miniaturized laser module[3] can be incorporated into a wider range of equipment.
- The use of a newly developed phosphor material has increased blue light emissions by 40%*3, contributing to the realization of a 10,000-lumen class high-luminous flux white light source through the red, green and blue phosphors.
- The generation of red, green and blue lights from only one type of laser light using a rotating phosphor wheel[4] simplifies the optical system and ensures that the laser is projected directly onto the screen.
This development is based on the following new technologies:
- High-output, low-loss laser design technique with wider near-ultraviolet laser optical waveguide and optimized light loss control.
- Phosphor material technology that utilizes the high-density crystalline structure of SMS (Sr3MgSi2O8) phosphor to control the density of the luminescent center and thus prevent luminous saturation.
- Wavelength conversion technology that uses a rotating phosphor wheel that absorbs near-ultraviolet laser light and converts it to red, green and blue luminescent light.
Conventional laser white light sources require multiple visible light semiconductor lasers that emit blue and other colors, which creates a tradeoff between small form factor and high brightness. Some laser wavelengths are even projected directly, without passing through the phosphor material. Conventional phosphors are not suitable for use as high-intensity light sources, as they are subject to significant luminance saturation when laser light is focused on them.
Panasonic holds 39 patents in Japan and 22 overseas patents, including pending applications, for this development.
This newly developed technology received the Distinguished Paper Award from the Society for Information Display (SID), the world's largest international conference for displays and related products. Panasonic will present this new technology at the 2013 SID International Symposium to be held in Vancouver, Canada from May 21 to 24.
*1 In comparison with conventional models developed by Panasonic.
*2 For a near-ultraviolet laser, as of May 24, 2013. Survey by Panasonic.
*3 When irradiated with 60-watt near-ultraviolet semiconductor laser light.
Explanation of technical terms
- [1] Lumen
- The unit of light flux in the International System of Units.
- [2] Luminance Saturation
- The phenomenon where optical power may decline as the intensity of incident radiation increases.
- [3] Laser Module
- Refers to a component where two or more semiconductor lasers are mounted and which functions as a light source.
- [4] Phosphor Wheel
- A component where light is shined onto the surface of a disc, onto which phosphor has been applied, which is then rotated by a motor on the central shaft, continuously creating phosphor light.
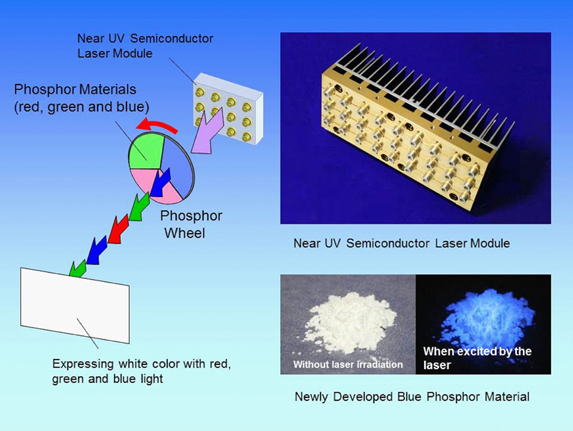
Conceptual Diagram of the Newly Developed White Light Source
About Panasonic
Panasonic Corporation is a worldwide leader in the development and engineering of electronic technologies and solutions for customers in residential, non-residential, mobility and personal applications. Since its founding in 1918, the company has expanded globally and now operates over 500 consolidated companies worldwide, recording consolidated net sales of 7.30 trillion yen for the year ended March 31, 2013. Committed to pursuing new value through innovation across divisional lines, the company strives to create a better life and a better world for its customers. For more information about Panasonic, please visit the company's website at http://panasonic.net/.






