Panasonic has a long history of introducing cutting-edge technology to the battery field since the introduction of its dry cell battery for bullet-shaped battery-powered lamps in 1923. Continuing to innovate over the next 100 years, Panasonic produced the nickel-cadmium battery in 1964, developed the nickel-metal hydride battery in 1989, and more recently developed the lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery in 1994 and provided Li-ion batteries for automotive use in 2008. It currently holds more than 7,500 patents for material development and manufacturing in battery-related fields, and has had zero recalls resulting from its automotive Li-ion batteries, making the company a leader in the industry with a reliable track record and advanced technological capabilities.
The potential uses of batteries are growing exponentially as industries and consumers look for ways to lower carbon emissions. The company estimates that the market for automotive business will grow by 5 trillion yen and industry and consumer business by 600 billion yen from 2020 to 2025. To meet future demand, Panasonic Energy has been expanding and diversifying its battery products for different industries and consumer use as well as the automotive industry.
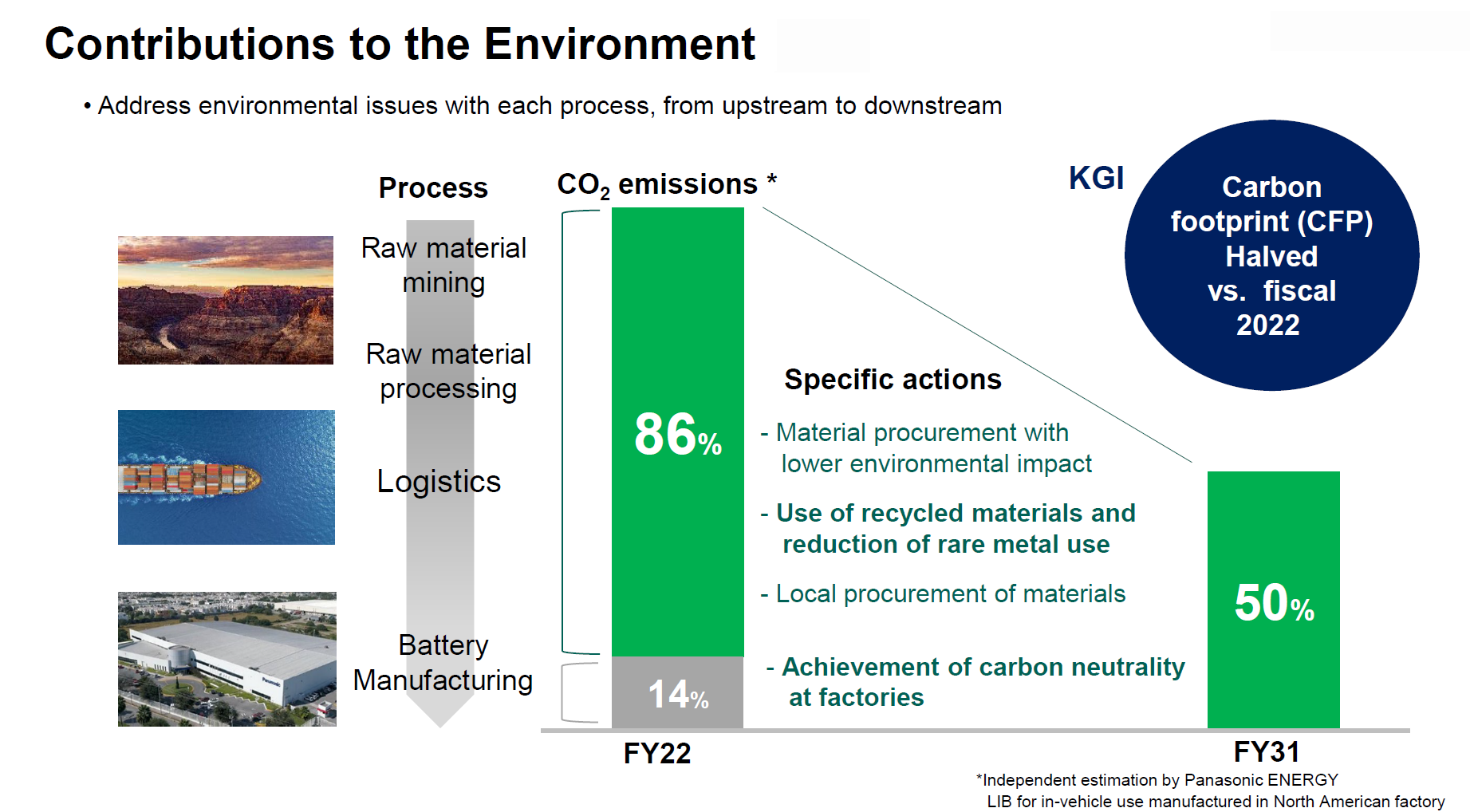
In the automotive business, Panasonic Energy has supplied a cumulative total of more than 10 billion cells of cylindrical Li-ion batteries for EVs, equivalent to 1.7 million EVs, which supports the electrification of mobility and helps to reduce CO2 emissions. As consumers look to reduce environmental impact with the use of EVs, Panasonic Energy will continue to contribute to the evolution and popularization of EVs with its technological capabilities.
Safety and reliability are paramount when supplying energy solutions and batteries to infrastructure-related sectors. Panasonic Energy has been leading in the development of secure battery supplies to promote electrification and digitalization of our society. The company will continue to maximize its usefulness and value by applying its expertise in its core technology in battery cells to expand the solutions offered to the industrial and consumer fields. Related opportunities include information and communications infrastructure such as data centers, power equipment such as assisted bicycles, construction and agricultural machinery, and IoT devices such as smart meters and medical equipment.