
Mar 11, 2026
- Products & Solutions
- Stories
- Technology
- AI & Robotics
- CES
- Business Solutions
- Electronic Materials/Devices
Jun 23, 2021
Products & Solutions / Press Releases
Osaka, Japan - Panasonic Corporation joined Mori Building Company, Limited (Headquarters: Minato, Tokyo; President and CEO: Shingo Tsuji. Hereinafter referred to as "Mori Building") and eHills Corporation (Headquarters: Minato, Tokyo; CEO: Hiroo Mori. Hereinafter referred to as "eHills") to build a virtual private network consisting of a private telephone network using sXGP*1 base stations, a private 4G (LTE) standard using unlicensed frequency bands, with a 5G core network (hereinafter referred to as "5G core") and a public LTE network, and conducted a demonstration experiment with the purpose of developing new services for building tenants and facilities, and off-site environments.
In this virtual private network, users of building tenants who use offices in large cities, satellite offices, and shared offices can connect directly to the intranet of their companies securely at anytime from anyplace without being concerned about where they are and without being worried about complicated setup such as VPN connection settings. In addition, by developing sXGP base stations connected to the 5G core as a building infrastructure and utilizing 5G network slicing, the private telephone network will be further expanded as a communication platform for the building operation and management system, etc. This system is designed to go beyond the premises of each building, with an eye toward supporting autonomous driving in an area of several buildings. After extracting the effects and issues of sXGP, we are planning to replace some base stations with local 5G stations and carry out a demonstration to sophisticate the system.
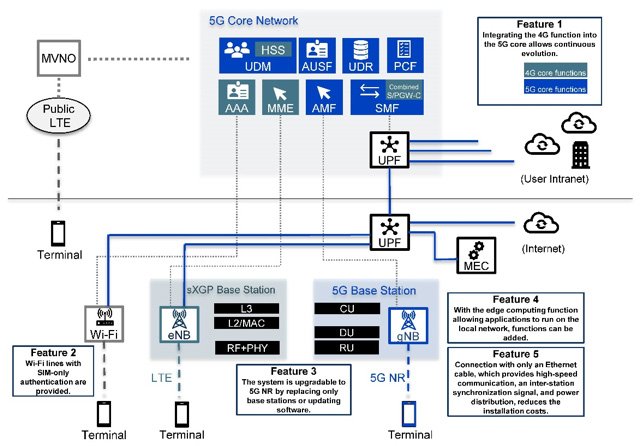 Fig.1 System configuration image
Fig.1 System configuration image
Under today's COVID-19 pandemic, there is demand for a secure, stress-free, and cost-effective business network, which gives the users office levels of work efficiency and information security in any location, including satellite offices, shared offices, public places, homes, and workation spots. Exploring networks for building tenants that respond to the changing business environment and networks for efficient remote management of buildings, this demonstration experiment, which is scheduled from April to December 2021, is intended to verify the network's usefulness, practicality, and cost effectiveness, while further improving its performance. After the end of this demonstration period, we plan to launch commercial services based on the results. The network built for this experiment is based on sXGP, a type of 4G LTE, an international mobile phone standard, that allows device installation without a license. The equipment is shared among the tenants but can be individually connected to the intranet of each tenant company. This technology also allows secure wireless connection of many devices. The experiment will check these functions, and verify the possibility of digital transformation of building operations including tenant services and building management.
The experimental network will inherit the features of the Personal Handy-phone System (PHS), which is a low-cost reliable private telephone system with many years of service history. In a disaster situation, PHS communication in premises can be maintained without being affected by the state of the external network. The new network will serve as a company IoT network with PHS's high reliability. Through this network, multifunctional smartphones and personal computers, and IoT devices can be securely connected under robust security management, integrating the conventional private telephone network and the private IP information network. The sXGP base stations are operated with the 5G core network we have developed. By updating the software, the system allows continuous infrastructure investment for future deployment of 5G-specific applications such as a more interactive CPS*2 environment, sophisticated building automation, and auto valet parking*3 in the building's car park. A system with such an architecture has the following features.
Through this demonstration experiment, we will work toward the automation of building management, remote monitoring of building facilities from home, etc., and creation of healthy, secure, and safe business spaces for building tenants, and will support the digital transformation of the building operation business.
Panasonic Corporation Brand Strategy Division Corporate PR Department
https://news.panasonic.com/global/contacts/
Panasonic Corporation is a global leader developing innovative technologies and solutions for wide-ranging applications in the consumer electronics, housing, automotive, and B2B sectors. The company, which celebrated its 100th anniversary in 2018, operates 522 subsidiaries and 69 associated companies worldwide and reported consolidated net sales of 6,698.8 billion yen for the year ended March 31, 2021. Committed to pursuing new value through collaborative innovation, the company uses its technologies to create a better life and a better world for customers. Learn more about Panasonic: https://www.panasonic.com/global.
The content in this website is accurate at the time of publication but may be subject to change without notice.
Please note therefore that these documents may not always contain the most up-to-date information.
Please note that German, Spanish and Chinese versions are machine translations, so the quality and accuracy may vary.